Python Data Cleaning Library
Robust Python library for data cleaning process for Data Science projects.
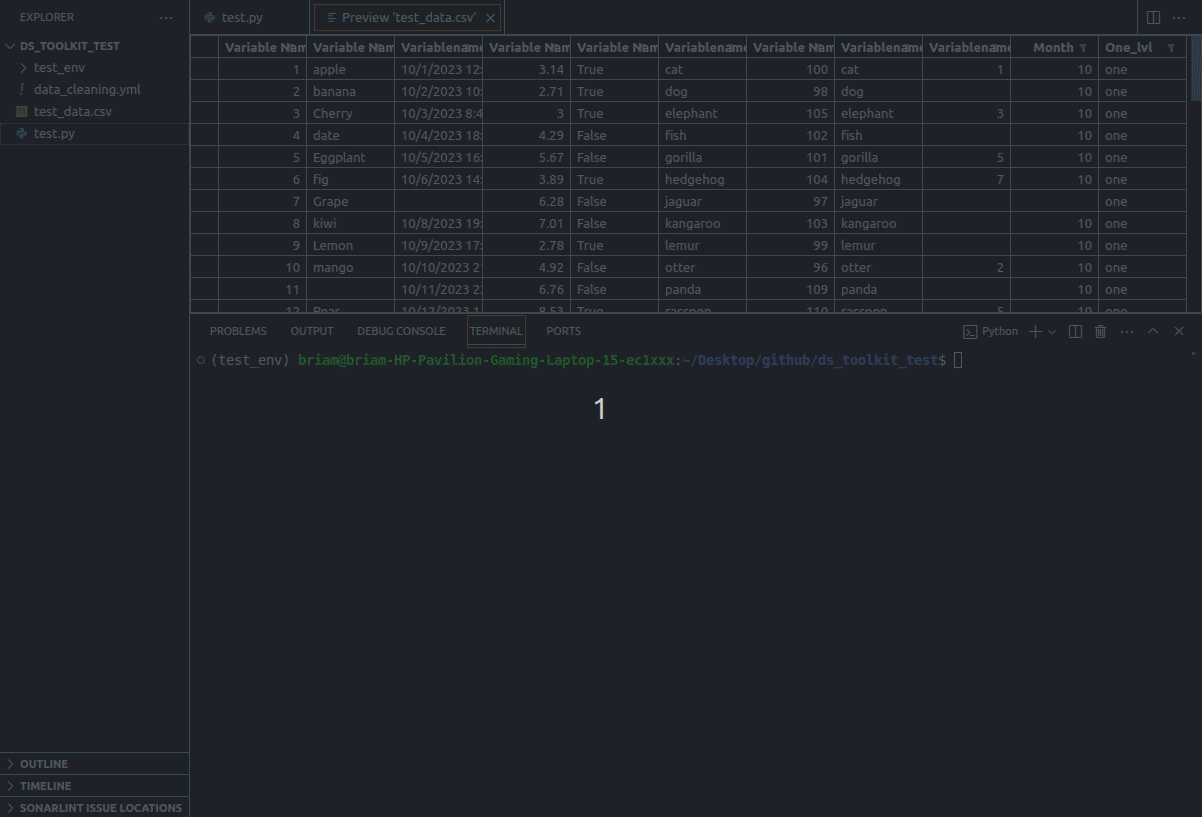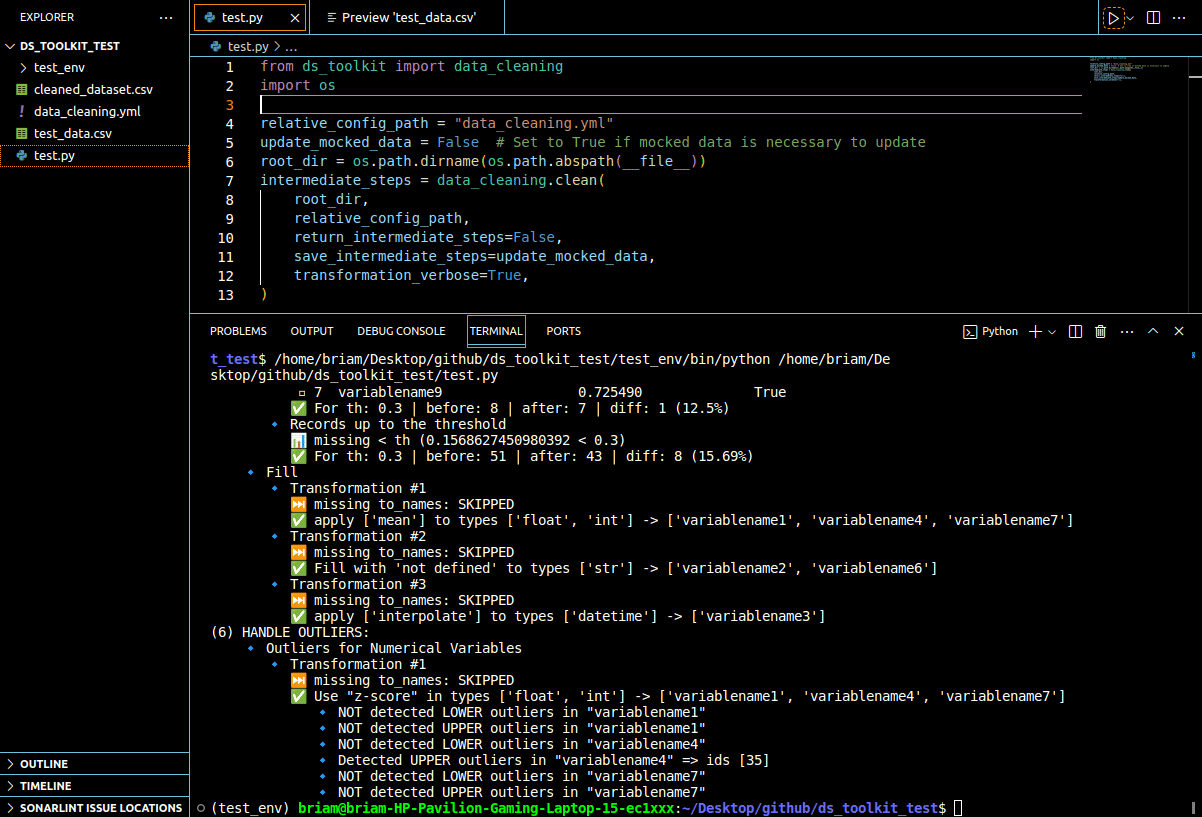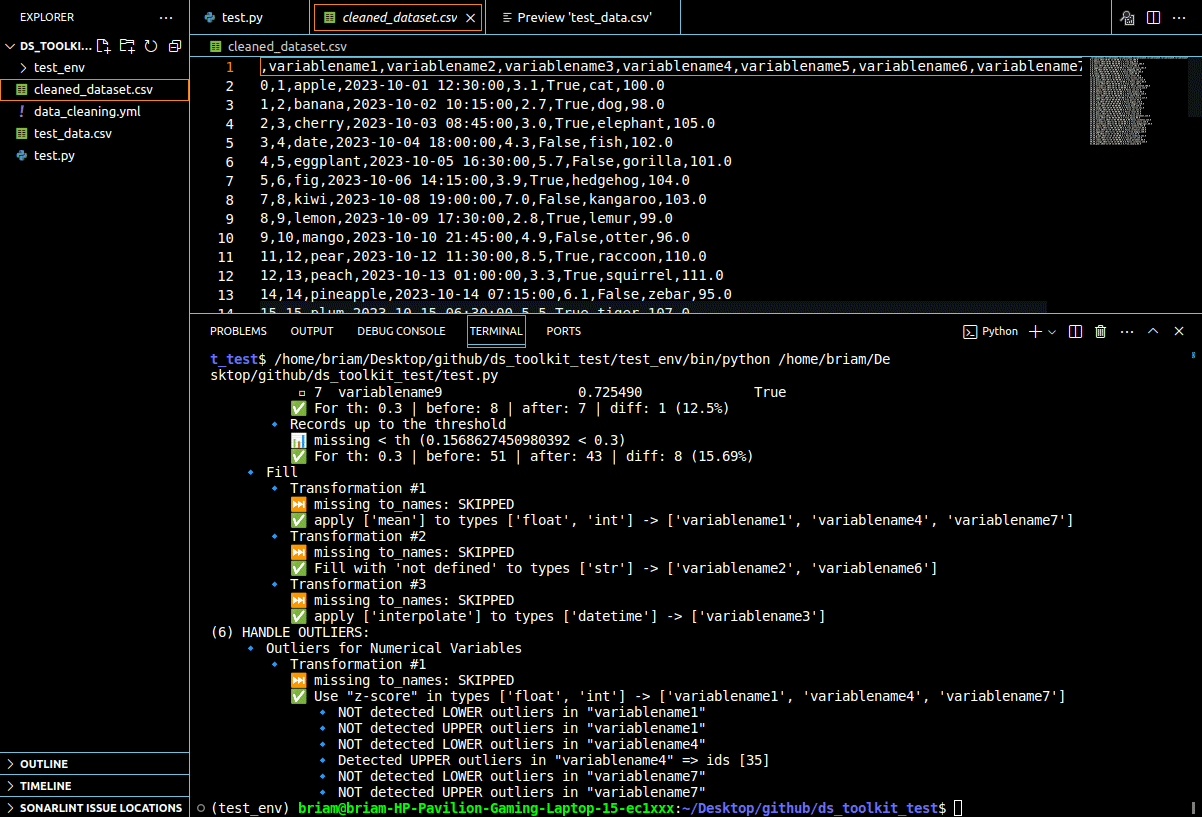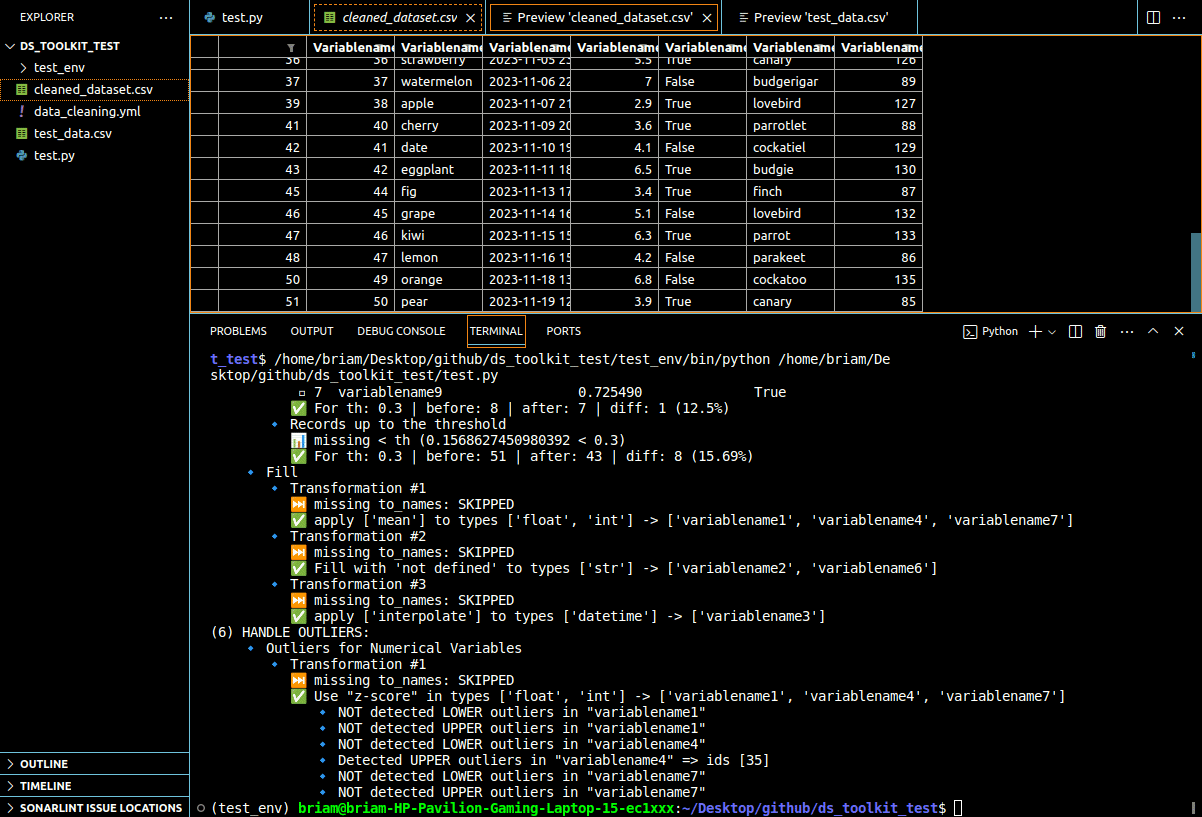
The Data Cleaning Library provides a convenient way to automate the data cleaning process. It uses a YAML configuration file to specify various cleaning stages and parameters. Below is an example of how to use the library and an explanation of the YAML configuration file.
Documentation
Example Usage
import os
from ds_toolkit.data_cleaning import clean
root_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
relative_config_path = "data_cleaning.yml"
intermediate_steps = clean(
root_dir,
relative_config_path,
)YAML Configuration File (data_cleaning.yml)
general:
input: 'test_data.csv'
output: 'cleaned_dataset.csv'
stages:
prepare:
variable_names:
apply: 'lower'
variable_values:
- apply:
function: ['lower']
params:
digits_to_round: null
to:
variable_types: ['str']
variable_names: null
remove_duplicate:
records: true
variables: true
remove_irrelevant:
one_level_variables: true
redundant_variables: ['month']
handle_missing_data:
remove:
variables_threshold: 0.3
records_threshold: 0.3
fill:
- apply:
fill_method: ['mean']
value: null
to:
variable_types: ['float', 'int']
variable_names: null
handle_outliers:
numerical:
- detect:
method: 'z-score'
apply:
lower: 'quantile'
upper: 'quantile'
lower_limit: null
upper_limit: null
to:
variable_types: ['float', 'int']
variable_names: nullYAML Configuration Explanation
General Section
- input: Path to the input dataset (CSV format).
- output: Path to save the cleaned dataset (CSV format).
Stages Section
1. Prepare (Optional)
-
variable_names (Optional): Apply case conversion to variable names.
- apply: Specify the case conversion (‘upper’ or ‘lower’).
-
variable_values (Optional): Apply transformations to variable values.
- apply: Specify the transformation function(s) (‘int’, ‘str’, ‘float’, ‘bool’, ‘round’, ‘upper’, ‘lower’, ‘datetime’).
- params: Parameters for the transformation function(s).
2. Remove Duplicate (Optional)
- records: Remove duplicate records if set to
true. - variables: Remove duplicate variables if set to
true.
3. Remove Irrelevant (Optional)
- one_level_variables: Remove one-level variables if set to
true. - redundant_variables: Specify a list of redundant variable names to be removed.
4. Handle Missing Data (Optional)
-
remove: Remove variables or records with missing data based on specified thresholds.
- variables_threshold: Threshold for removing variables with missing data.
- records_threshold: Threshold for removing records with missing data.
-
fill: Fill missing data using various methods.
- apply: Specify the fill method(s) (‘bfill’, ‘ffill’, ‘mean’, ‘median’, ‘mode’, ‘interpolate’, ‘remove-r’).
- value: Value to fill missing data with (if applicable).
- to: Specify the variable types and names to apply the fill method.
5. Handle Outliers (Optional)
- numerical: Handle outliers for numerical variables.
- detect: Specify the detection method (‘z-score’, ‘iqr’).
- apply: Specify the action for outliers (‘remove-r’, ‘quantile’, ‘mean’).
- lower: Specify the lower bound action.
- upper: Specify the upper bound action.
- lower_limit: Specify the lower limit for outliers.
- upper_limit: Specify the upper limit for outliers.
- to: Specify the variable types and names to apply outlier handling.
Adjust the parameters and stages based on specific data cleaning requirements.
Output
(1) PREPARE VARIABLE NAMES:
✅ variable names transformed to LOWER
(2) PREPARE VARIABLE VALUES:
🔹 Transformation #1
⏭ missing to_names: SKIPPED
✅ apply ['lower'] to types ['str'] -> ['variablename2', 'variablename3', 'variablename6', 'variablename8', 'one_lvl']
🔹 Transformation #2
✅ apply ['datetime'] to ['variablename3']
⏭ missing to_types: SKIPPED
🔹 Transformation #3
⏭ missing to_names: SKIPPED
✅ apply ['round'] to types ['float'] -> ['variablename4', 'variablename7', 'variablename9', 'month']
(3) HANDLE DUPLICATE DATA:
🔹 Remove duplicate records
✅ before: 52 | after: 51 | diff: 1 (1.92%) => ids [13]
🔹 Remove duplicate variables
✅ before: 11 | after: 10 | diff: 1 (9.09%) => ['variablename8']
(4) HANDLE IRRELEVANT DATA:
🔹 Remove one level variables
✅ before: 10 | after: 9 | diff: 1 (10.0%) => ['one_lvl']
🔹 Remove redundant variables
✅ before: 9 | after: 8 | diff: 1 (11.11%) => ['month']
(5) HANDLE MISSING DATA:
🔹 Remove
🔹 Variables up to the threshold
📊 Variable Missing Data Proportion Greater than th?
▫ 0 variablename1 0.000000 False
▫ 1 variablename2 0.058824 False
▫ 2 variablename3 0.058824 False
▫ 3 variablename4 0.019608 False
▫ 4 variablename5 0.000000 False
▫ 5 variablename6 0.078431 False
▫ 6 variablename7 0.019608 False
▫ 7 variablename9 0.725490 True
✅ For th: 0.3 | before: 8 | after: 7 | diff: 1 (12.5%)
🔹 Records up to the threshold
📊 missing < th (0.1568627450980392 < 0.3)
✅ For th: 0.3 | before: 51 | after: 43 | diff: 8 (15.69%)
🔹 Fill
🔹 Transformation #1
⏭ missing to_names: SKIPPED
✅ apply ['mean'] to types ['float', 'int'] -> ['variablename1', 'variablename4', 'variablename7']
🔹 Transformation #2
⏭ missing to_names: SKIPPED
✅ Fill with 'not defined' to types ['str'] -> ['variablename2', 'variablename6']
🔹 Transformation #3
⏭ missing to_names: SKIPPED
✅ apply ['interpolate'] to types ['datetime'] -> ['variablename3']
(6) HANDLE OUTLIERS:
🔹 Outliers for Numerical Variables
🔹 Transformation #1
⏭ missing to_names: SKIPPED
✅ Use "z-score" in types ['float', 'int'] -> ['variablename1', 'variablename4', 'variablename7']
🔹 NOT detected LOWER outliers in "variablename1"
🔹 NOT detected UPPER outliers in "variablename1"
🔹 NOT detected LOWER outliers in "variablename4"
🔹 Detected UPPER outliers in "variablename4" => ids [35]
🔹 NOT detected LOWER outliers in "variablename7"
🔹 NOT detected UPPER outliers in "variablename7"This documentation provides a comprehensive guide on using the data cleaning library and customizing the cleaning process according to specific requirements.
Technology Stack
Python (Numpy, Pandas and Pytest)
The core programming language used to develop the library and build unit testing.